Transportation Systems Analysis Model (TSAM)
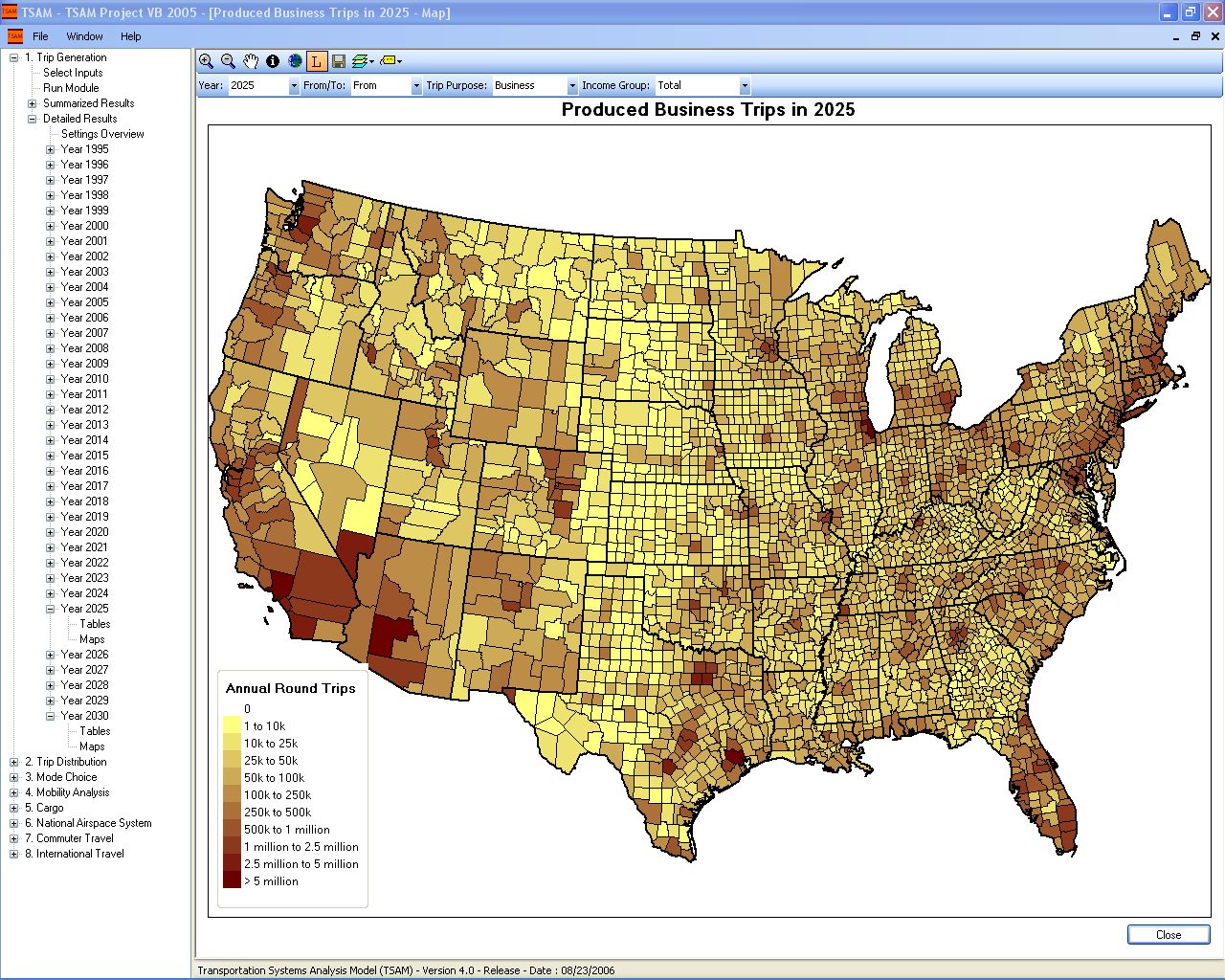
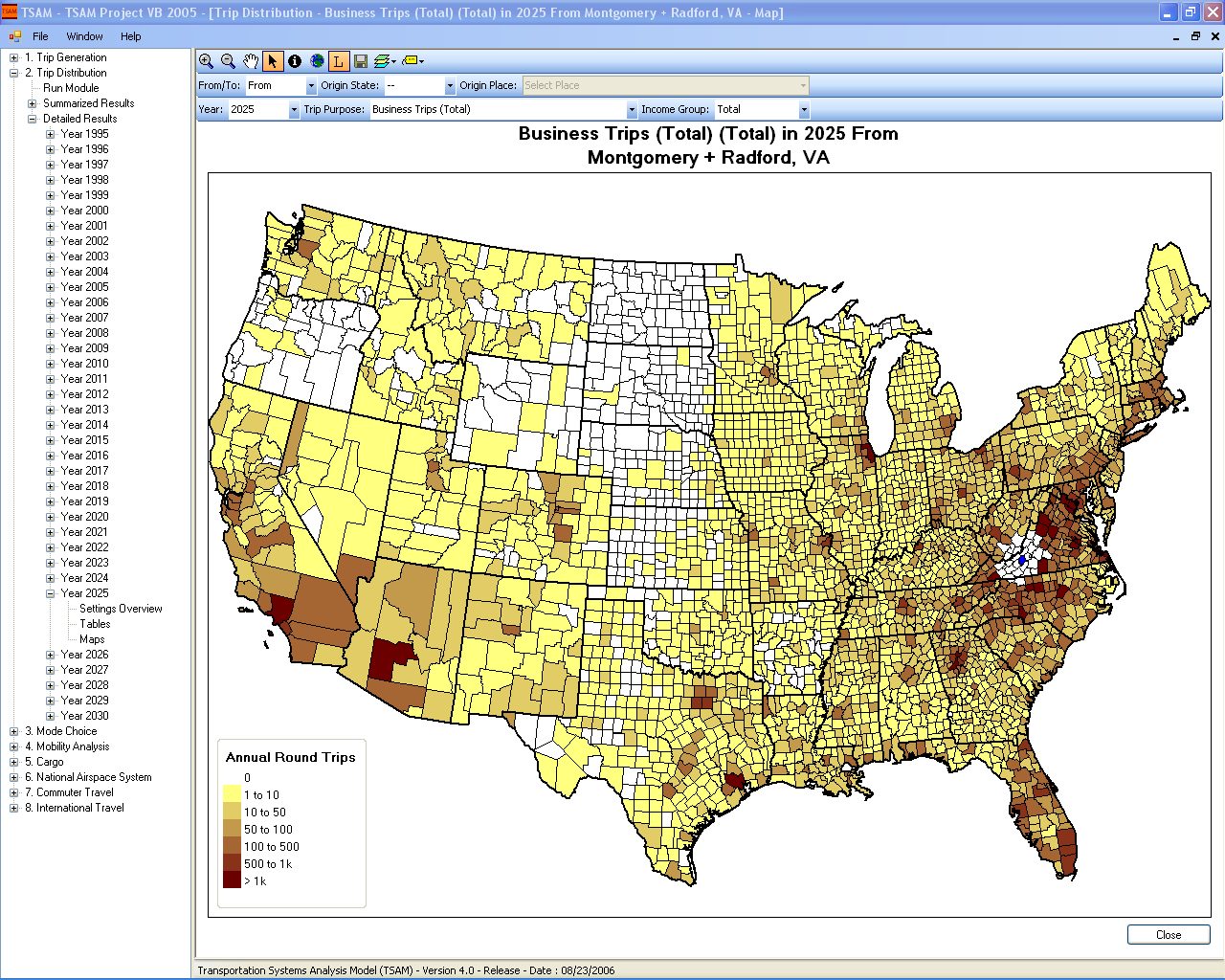
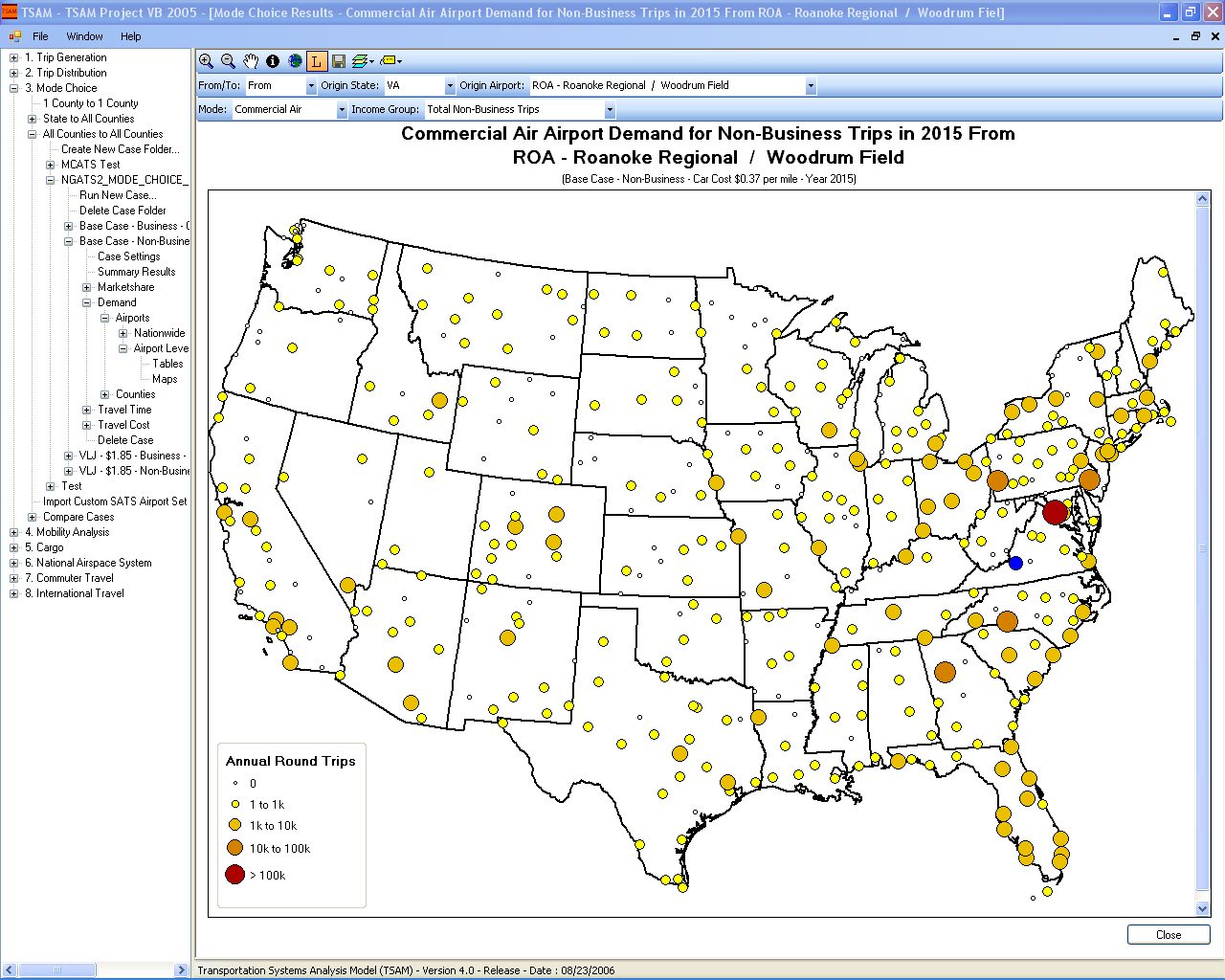
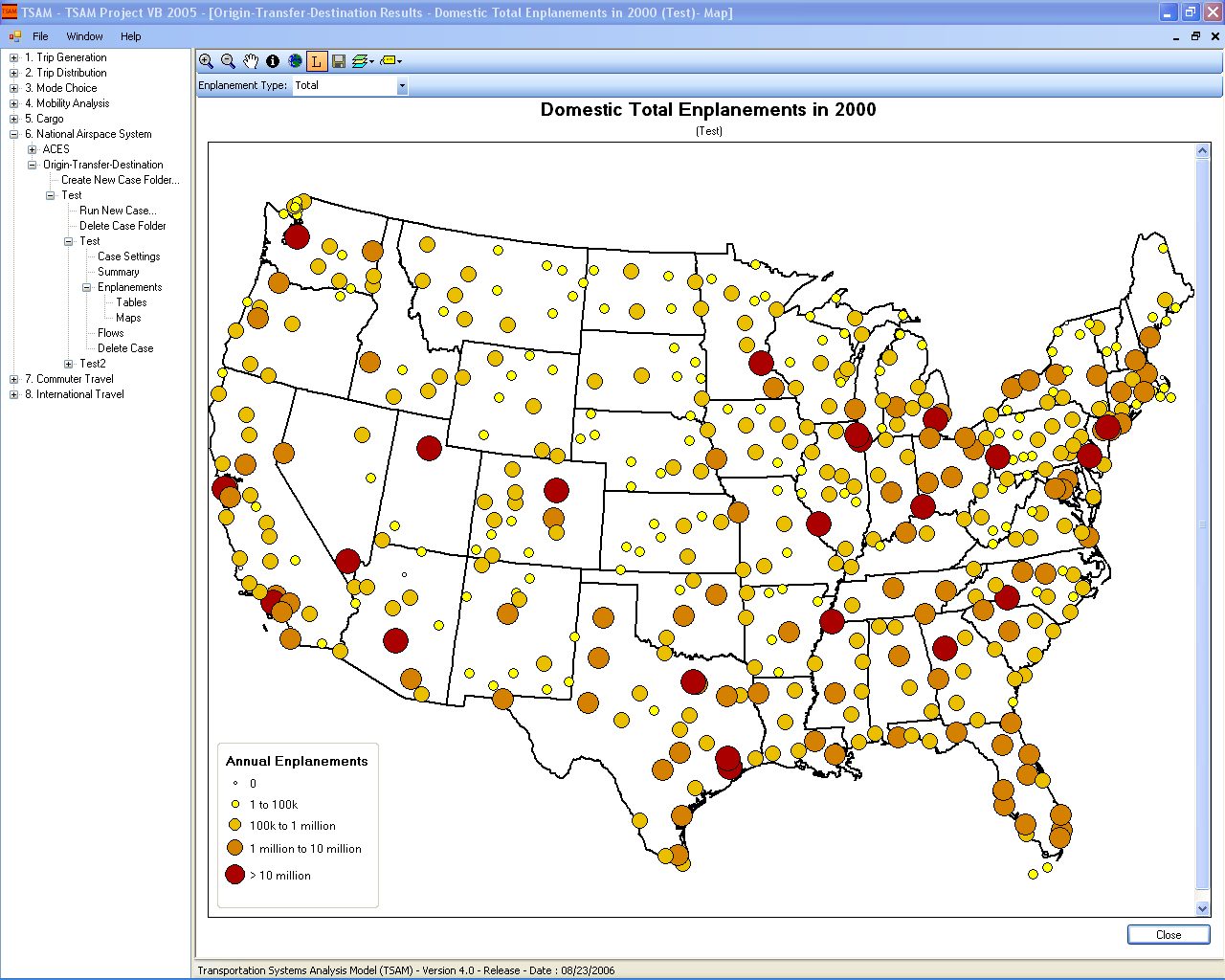
TSAM is a nationwide transportation planning model to forecast intercity travel behavior in the United States. It can be used to analyze the impact of transportation policy changes and the introduction of new modes of transportation to the existing transportation system. Mode specific metrics such as travel cost, travel time and generated revenue can be extracted and analyzed to measure the effects of such changes. Today it can forecast the automobile, commercial airline, air taxi and rail demand up to the year 2030 between all the counties in the United States. The commercial airline and air taxi demand is also reported at the airport level and at the station level for rail. Finally, the impacts on the National Airspace System can also be assessed with TSAM by using its output in conjunction with air traffic simulation software to model the commercial airline and air taxi traffic in the future.
Features
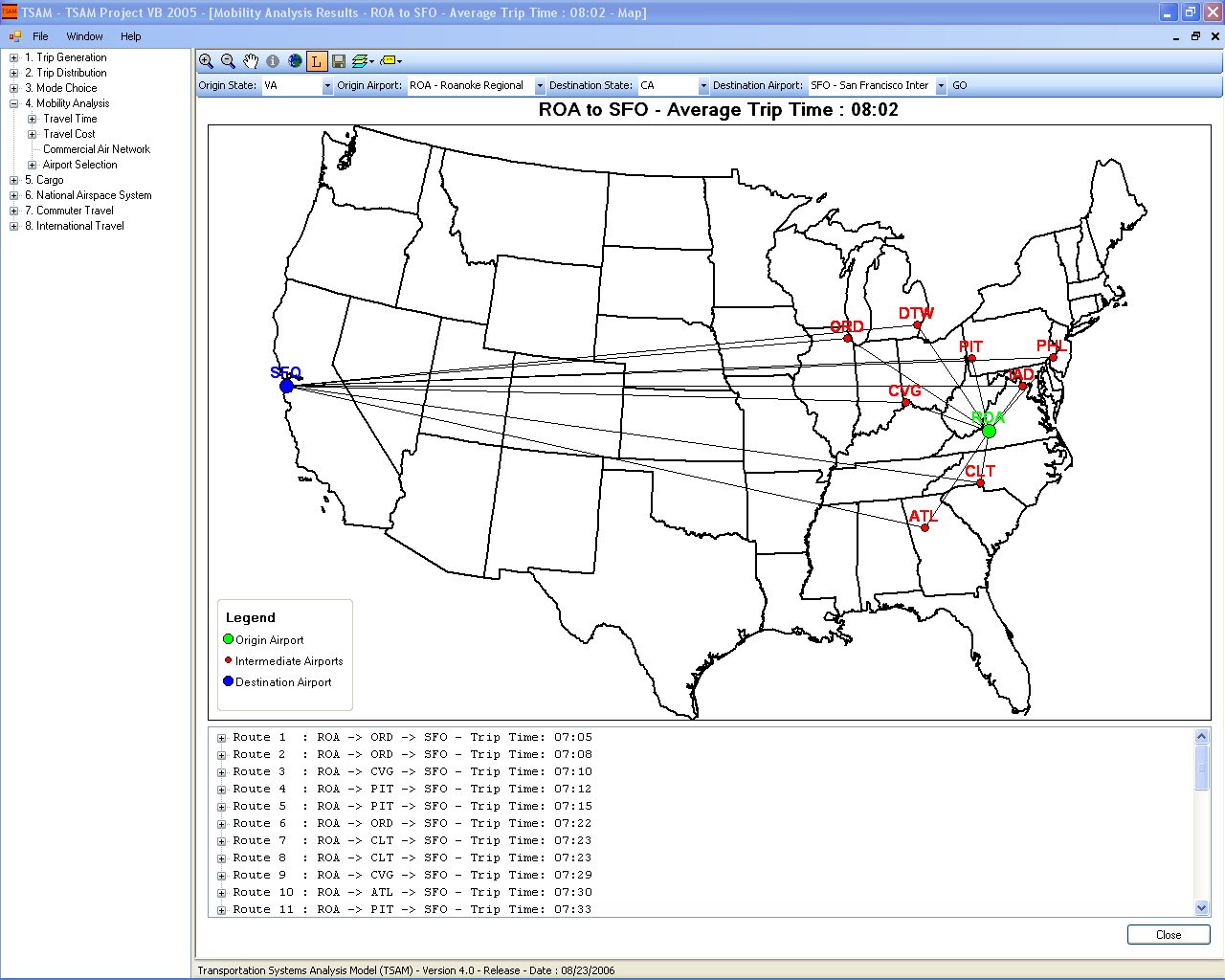
- County-to-county intercity passenger demand for automobile, commercial airline, air taxi and rail.
- Airport-to-airport passenger demand for commercial airline and air taxi.
- Demand estimated for:
- Up to year 2030.
- Two trip purposes (Business and Non-Business).
- Five household income groups (<$30K, $30K-$60K, $60K-$100K, $100K-$150K, >$150K).
- Revenue forecasts for all modes.
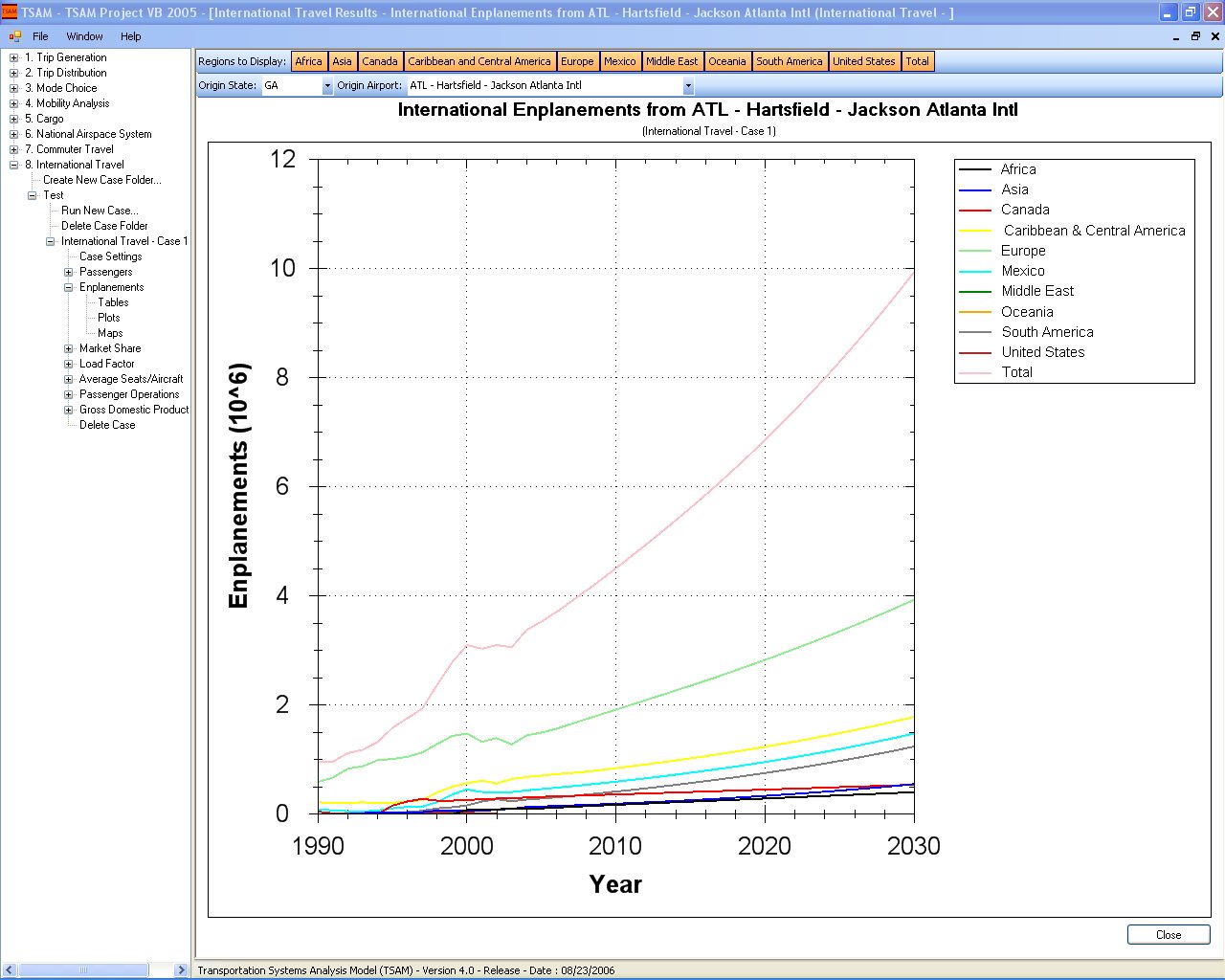
- Commercial airline domestic and international enplanements at commercial airports.
- Commercial airline passenger route/network flows.
- Commercial airline and air taxi revenue passenger miles (RPM) calculations.
- Air cargo demand at the county and airport level.
- Airport capacity estimatations.
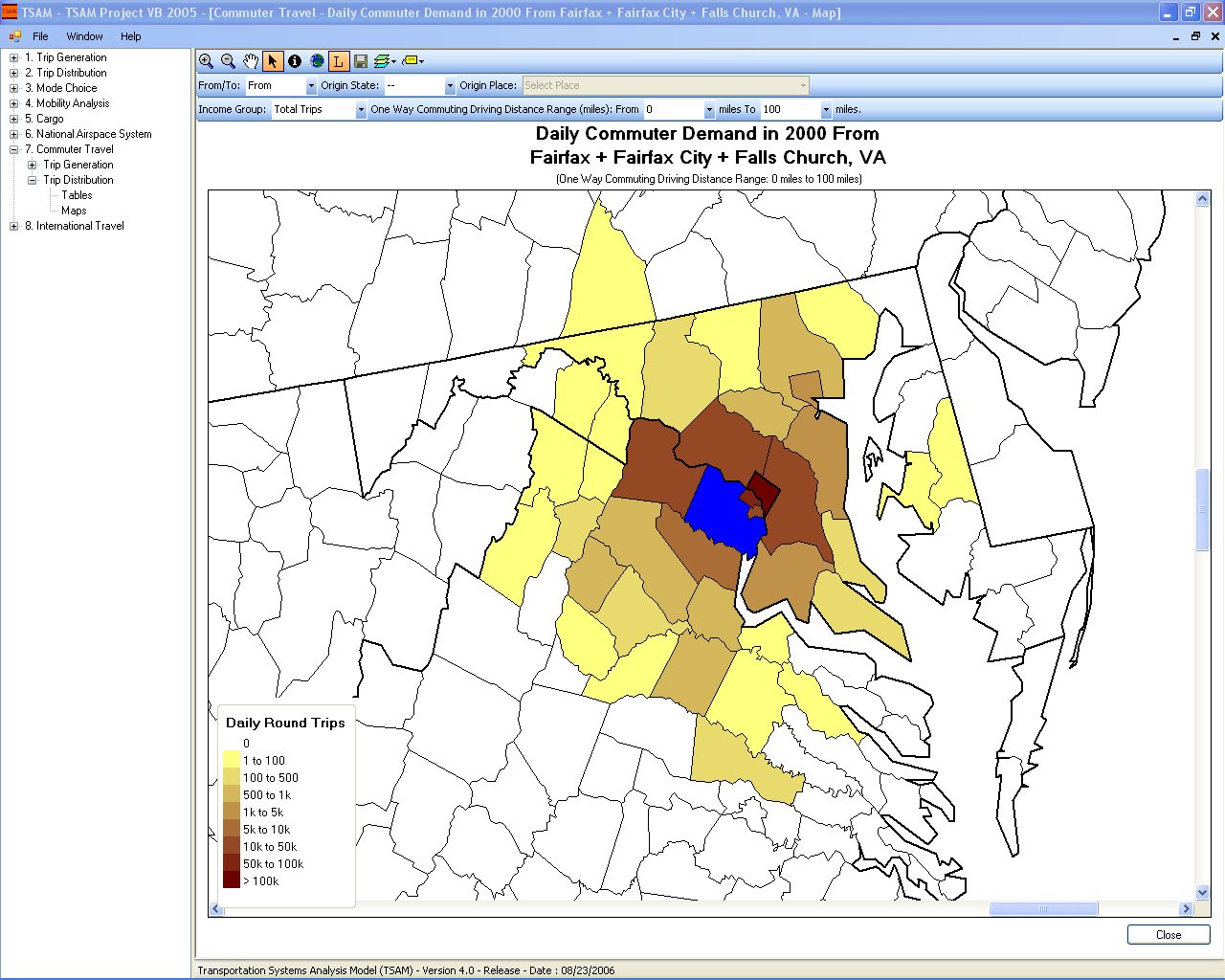
- Commuter travel forecast up to the year 2030.
- Integration with air traffic simulation models such as the Airspace Concept Evaluation Sytems (ACES).
Benefits
- Estimate the impacts of new policies on the transportation system by evaluating the difference in the metrics.
- Estimate the impacts of the introduction of a new mode of transportation such as the Very Light Jet (VLJ) at airports and in the National Airspace System (NAS).
- Predict the interactions between the different modes of transportation when travel cost and travel time vary due to socio-economic changes such as fuel cost and inceased security at commercial airports.
- Forecast the changes in ground noise and pollutant emissions due to changes in the air traffic demand at airports.
- Generate cost/benefit analyses for various transportation systems planning scenarios.
Associated Publications
- A Transportation Systems Analysis Model (TSAM) to study the impact of the Small Aircraft Transportation System (SATS) (2005)
- Development of a Decision Support Model Using MapObjects to Study Transportation Systems (2004)
- Integrated Model To Study The Small Aircraft Transportation System (SATS) (2003)